
| 📰 Title: | FluidSynth | 🕹️ / 🛠️ Type: | Tool |
|---|---|---|---|
| 🗃️ Genre: | Development | 👁️ Visual: | 2D |
| 🏷️ Category: | Development ➤ Audio Production ➤ Synthesizer | 🏝️ Perspective: | First person (interface) |
| 🔖 Tags: | Development; Audio Production; Synthesizer; Soundfonts; MIDI; Flagship | ⏱️ Pacing: | Real Time |
| 🐣️ Approx. start: | 2003-03-09 | 👫️ Played: | Single |
| 🐓️ Latest: | 2024-03-26 | 🚦 Status: | 04. Released (status) |
| 📍️ Version: | Latest: 💥️ 2.3.5 / Dev: db86c36 | ❤️ Like it: | 9. ⏳️ |
| 🏛️ License type: | 🕊️ Libre | 🎀️ Quality: | 7. ⏳️ |
| 🏛️ License: | LGPL-2.1 | ✨️ (temporary): | |
| 🐛️ Created: | 2014-02-09 | 🐜️ Updated: | 2024-06-17 |
| 📦️ Package name: | fluidsynth, fluidsynth-dssi, qsynth | ..... 📦️ Arch: | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 📄️ Source: | ..... 📦️ RPM: | ||
| ⚙️ Generic binary: | ..... 📦️ Deb: | ||
| 🌍️ Browser version: | ..... 📦️ AppImage: | ||
| 📱️ PDA support: | ..... 📦️ Flatpak: | ||
| ✨️ Not use: | ..... 📦️ Snap: |
| 📰 What's new?: | 👔️ Already shown: | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| 💡 Lights on: | 💭️ New version published (to be updated): | ||
| 🎨️ Significant improvement: | 🦺️ Work in progress: | ||
| 🎖️ This work: | 🚧️ Some work remains to be done: | ||
| 👫️ Contrib.: | goupildb & Louis | 👻️ Temporary: | |
| 🎰️ ID: | 14173 |
| 📜️[en]: | A libre, multi-platform, command line synthesizer based on the SoundFont 2 & 3 (= 2 compressed in Vorbis) standard to interpret MIDI (Musical Instrument Digital interface) commands from a MIDI device or file. External graphical interfaces are also available (Qsynth, gmf_synth). On the other hand, FluidSynth-DSSI is a modification of FluidSynth, allowing it to be used as a plugin (in server mode) and thus to be integrated into sound processing chains. | 📜️[fr]: | Un synthétiseur libre et multi-plateforme en ligne de commande, s'appuyant sur la norme SoundFont 2 et 3 (= 2 compressée en Vorbis) pour interpréter des commandes MIDI (Musical Instrument Digital interface) issues d'un périphérique ou fichier MIDI. Des interfaces graphiques externes sont aussi disponibles (Qsynth, gmf_synth). D'autre part, FluidSynth-DSSI est une modification de FluidSynth, permettant de l'utiliser sous forme de plugin (en mode serveur) et ainsi de l'intégrer dans des chaînes de traitement sonore. |
|---|
🦝️ From Users: (201007),
🕯️ How To: (202005), (202006),
🎮️ Showcase: (202004), (201202), (201708),
🐧 Linux plays: (201109),
🏡️ Website & videos
[Homepage 1 2] [Dev site 1 2] [Features/About 1 2] [Screenshots 1 2] [Videos t(202xxx) gd(202xxx) r(201007) lp(201109) ht(202005) ht(202006) d(202004) d(201202) d(201708) d(201711) d(202004) d(202004) d(202108) d(202004) d(201602) d(201711) g[fr](202xxx) g[de](202xxx) g[ru](201701) g[pl](202xxx) g[cz](202xxx) g[sp](202xxx) g[pt](202xxx) g[it](202xxx) g[tr](202xxx)] [WIKI 1 2] [FAQ] [RSS] [Changelog 1 2 3]
💰 Commercial
• (empty)
🍩️ Resources
• Some GUI for FluidSynth: [Qsynth (Qt GUI) 1 2] [gmf_synth (Python GUI)]
🛠️ Technical informations
[Open Hub] [PCGamingWiki] [MobyGames] [Showcase]
🦣️ Social
Devs (FluidSynth Team 1 2 3 [fr] [en]): [Site 1 2] [Chat] [mastodon] [PeerTube] [YouTube] [PressKit] [Interview 1(202xxx) 2(202xxx)]
The Project: [Blog] [Chat] [Forums] [mastodon] [PeerTube] [YouTube] [PressKit] [reddit] [Discord]
🐝️ Related
[Wikipedia (FluidSynth) [fr] [en] [de]]
[Wikipedia (DSSI) [fr] [en] [de]]
[FreshFOSS]
📦️ Misc. repositories
• FluidSynth: [Repology 1 2] [pkgs.org] [Generic binary] [Arch Linux / AUR] [openSUSE] [Debian/Ubuntu 1 2] [Flatpak] [AppImage(author's repo)] [Snap] [PortableLinuxGames]
• Qsynth: [Repology] [pkgs.org] [Generic binary] [Arch Linux / AUR] [openSUSE] [Debian/Ubuntu] [Flatpak] [AppImage] [Snap] [PortableLinuxGames]
🕵️ Reviews
[HowLongToBeat] [metacritic] [OpenCritic] [iGDB]
🕊️ Source of this Entry: [Site (date)]
🦣️ Social Networking Update (on mastodon)
🛠️ Title: FluidSynth & Qsynth
🦊️ What's: A libre synthesizer (FluidSynth) & UI (Qsynth)
🏡️ https://www.fluidsynth.org
🐣️ https://github.com/FluidSynth
🔖 #LinuxGameDev #Flagship #Music #Synthesizer
📦️ #Libre #Arch #RPM #Deb #Flatpak #AppIm
📖 Our entry: https://www.lebottindesjeuxlinux.tuxfamily.org/en/online/lights-on/
🥁️ Update: 2.3.5
⚗️ Hotfix 🐞️
📌️ Changes: https://github.com/FluidSynth/fluidsynth/releases
🦣️ From: 🛜️ https://github.com/FluidSynth/fluidsynth/releases.atom
🦝️ https://www.youtube.com/embed/vdtWYsUSK8s
🕯️https://www.youtube.com/embed/wzIkIQ7Hebc
🎮️ https://www.youtube.com/embed/eOKqiLekYgY
🎮️ https://www.youtube.com/embed/4lNq0QRWs5U
🎮️ https://www.youtube.com/embed/35hIRRJ6bfQ
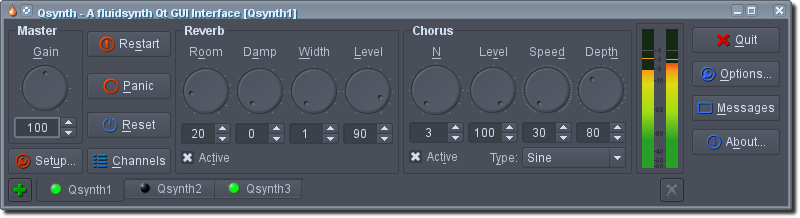
🕶️ A view of its IU (Qsynth), on a dark theme, with its potentiometers (reverb & chorus) and control knobs.
FluidSynth (& Qsynth UI) is a libre, multi-platform, command line synthesizer based on the SoundFont 2 & 3 (= 2 compressed in Vorbis) standard to interpret MIDI (Musical Instrument Digital interface) commands from a MIDI device or file. External graphical interfaces are also available (Qsynth, gmf_synth). On the other hand, FluidSynth-DSSI is a modification of FluidSynth, allowing it to be used as a plugin (in server mode) and thus to be integrated into sound processing chains.
📜️ "A libre command line synthesizer based on the SoundFont 2 standard to interpret MIDI commands from a MIDI device or file" 📜️ .
FluidSynth:
A SoundFont Synthesizer
FluidSynth is a real-time software synthesizer based on the SoundFont 2 specifications and has reached widespread distribution. FluidSynth itself does not have a graphical user interface, but due to its powerful API several applications utilize it and it has even found its way onto embedded systems and is used in some mobile apps.
Features
✅️ Cross platform support (Linux, macOS and Windows to name a few)
✅️ SoundFont 2 support
✅️ SoundFont 3 support (vorbis-compressed SF2)
✅️ Realtime effect control using SoundFont 2.01 modulators
✅️ Limited support for Downloadable Sounds (DLS) Level 1 & 2
✅️ Playback of MIDI files
✅️ Shared library which can be used in other programs
✅️ Built in command line shell
FluidSynth-DSSI:
DSSI (pronounced "dizzy") is an API for audio processing plugins, particularly useful for software synthesis plugins with user interfaces.
DSSI is an open and well-documented specification developed for use in Linux audio applications, although portable to other platforms. It may be thought of as LADSPA-for-instruments, or something comparable to VSTi.
DSSI consists of a C language API for use by plugins and hosts, based on the LADSPA API, and an OSC (Open Sound Control) API for use in user interface to host communications. The DSSI specification consists of an RFC which describes the background for the proposal and defines the OSC part of the specification, and a documented header file which defines the C API.
DSSI is Free Software. The DSSI header file is provided under the GNU Lesser General Public License.
🌍️ Wikipedia (FluidSynth) :
FluidSynth, formerly named iiwusynth, is a free open source software synthesizer which converts Musical Instrument Digital Interface (MIDI) note data into an audio signal using SoundFont technology without need for a SoundFont-compatible soundcard. FluidSynth can act as a virtual MIDI device, able to receive MIDI data from any program and transform it into audio on-the-fly. It can also read in SMF (.mid) files directly. On the output side, it can send audio data directly to an audio device for playback, or to a Raw or Wave file. It can also convert a SMF file directly to an audio file in faster-than-real-time. The combination of these features gives FluidSynth the following major use cases:
• Synthesizing MIDI data from another application directly to the speakers,
• Synthesizing MIDI data from another application, recording the output to an audio file,
• Playing a MIDI file to the speakers,
• Converting a MIDI file to a digital audio file.
The size of loaded SoundFont banks is limited by the amount of RAM available. There is a GUI for FluidSynth called Qsynth, which is also open source. Both are available in most Linux distributions, and can also be compiled for Windows. Windows binary installers are not distributed alone, though it is bundled with QSynth.
It features microtonal support and was used in the MicrotonalISM project of the Network for Interdisciplinary Studies in Science, Technology, and Music. A Max/MSP plugin is available from IRCAM.
The core synthesizer is written as a C library with a large application programming interface (API). Partial bindings for Python, Ruby, Haskell, and .NET Framework are available.
🌍️ Wikipedia (DSSI) :
Disposable Soft Synth Interface (DSSI) is a virtual instrument (software synthesizer) plugin architecture for use by music sequencer applications. It was designed for applications running under Linux, although there is nothing specific to Linux in the interface itself. It is distributed under the terms of a combination of GNU Lesser General Public License and some BSD licenses, all of which are free software licences.
Features
DSSI is sometimes described as Linux Audio Developer's Simple Plugin API (LADSPA) for instruments. LADSPA is an audio effects plugin architecture for filters, reverbs and other sound processing software tools, whereas DSSI was designed specifically for instrument plugins that generate sound from note events. DSSI extends LADSPA by adding note event delivery, but it also adds predefined program selections and a method for plugins to provide their own user interfaces, both of which may also be used by effects plugins. This is partly because DSSI was intended to be a lightweight addition to LADSPA that would require little extra effort from authors of LADSPA hosts and plugins to support, and partly to avoid distracting too much developer effort from the Generalized Music Plug-in Interface (GMPI) plug-in initiative (which has since stalled). Perhaps as a partial consequence of this early offhand approach to publicity, the number of DSSI plugins available remains small. A successor which reunites the two standards LADSPA and DSSI is LV2.
DSSI hosts on Linux can also host some Virtual Studio Technology (VST) instruments (VSTi) for Microsoft Windows using the dssi-vst wrapper plug-in, which in turn makes use of the Wine compatibility layer. The major programs supporting DSSI are Qtractor, Renoise and Rosegarden.
🍥️ Debian:
fluidsynth
Real-time MIDI software synthesizer
Fluidsynth is a real-time midi synthesizer based on the soundfont2 specifications. It can be used to render MIDI input or MIDI files to audio. The MIDI events are read from a MIDI device. The sound is rendered in real-time to the sound output device.
fluidsynth-dssi
DSSI wrapper for the FluidSynth SoundFont-playing synthesizer
The FluidSynth-DSSI package contains FluidSynth-DSSI, a wrapper for the FluidSynth SoundFont-playing software synthesizer, allowing it to function as a DSSI plugin.
DSSI is an API for audio processing plugins, particularly useful for software synthesis plugins with user interfaces.
Un synthétiseur logiciel temps réel basé sur les spécifications SoundFont 2, par la FluidSynth Team, initié par Josh Green & Peter Hanappe.
En C.
FluidSynth (ex Iiwusynth) est un synthétiseur libre et multi-plateforme en ligne de commande, s'appuyant sur la norme SoundFont 2 et 3 (= 2 compressée en Vorbis) pour interpréter des commandes MIDI (Musical Instrument Digital interface) issues d'un périphérique ou fichier MIDI. Des interfaces graphiques externes sont aussi disponibles (Qsynth, gmf_synth). D'autre part, FluidSynth-DSSI est une modification de FluidSynth, permettant de l'utiliser sous forme de plugin (en mode serveur) et ainsi de l'intégrer dans des chaînes de traitement sonore.
DSSI (prononcez "dizzy", aka "Disposable Soft Synth Interface") est une API / spécification pour les plugins d'instruments logiciels audios, dérivée de LAPSDA (et parfois surnommée "le LAPSDA des instruments").
LAPSDA (Linux Audio Developers Simple Plugin API) est l'équivalent Linuxien de VST (Virtual Sound Technology), une spécification assez répandue conçue à l'origine pour le séquenceur Cubase.
LAPSDA est une spécification conçue pour les filtres, les reverbs et autres outils logiciels de traitements sonores, tandis que DSSI est conçu spécifiquement pour les plugins générant des sons à partir d'évènements.
DSSI est particulièrement utile pour les plugins de synthétiseurs logiciels, permettant leur utilisation en mode serveur par les applications audio.
💡 Nota :
FluidSynth fonctionne nativement en ligne de commande, néanmoins il existe des interfaces dédiées (liens ci-dessus) :
• Qsynth : une interface développée avec la bibliothèque Qt,
• gmf_synth : une interface en Python.
FluidSynth:
Un synthétiseur SoundFont
FluidSynth est un synthétiseur logiciel en temps réel basé sur les spécifications de SoundFont 2 et a atteint une large diffusion. FluidSynth n'a pas d'interface utilisateur graphique, mais grâce à sa puissante API, plusieurs applications l'utilisent et il a même trouvé sa place sur des systèmes embarqués et est utilisé dans certaines applications mobiles.
Fonctionnalités
✅️ Support multi-plateforme (Linux, macOS et Windows pour n'en citer que quelques-uns)
✅️ Support de SoundFont 2
✅️ Support de SoundFont 3 (SF2 compressé en vorbis)
✅️ Contrôle des effets en temps réel à l'aide des modulateurs de SoundFont 2.01
✅️ Support limité pour les Sons téléchargeables (DLS) de niveau 1 et 2
✅️ Lecture de fichiers MIDI
✅️ Bibliothèque partagée qui peut être utilisée dans d'autres programmes
✅️ Shell intégré en ligne de commande
FluidSynth-DSSI:
DSSI (prononcé "dizzy") est une API pour les plugins de traitement audio, particulièrement utile pour les plugins de synthèse logicielle avec des interfaces utilisateur.
DSSI est une spécification ouverte et bien documentée développée pour être utilisée dans les applications audio Linux, bien qu'elle soit portable sur d'autres plateformes. Elle peut être considérée comme le LAPSDA des instruments, ou quelque chose de comparable à VSTi.
DSSI est constitué d'une API de langage C à utiliser par les plugins et les hôtes, basée sur l'API LADSPA, et d'une API OSC (Open Sound Control) à utiliser dans l'interface utilisateur pour héberger les communications. La spécification DSSI consiste en une RFC qui décrit l'arrière-plan de la proposition et définit la partie OSC de la spécification, ainsi qu'un fichier d'en-tête documenté qui définit l'API C.
DSSI est un logiciel libre. Le fichier d'en-tête DSSI est fourni sous la licence GNU Lesser General Public License.
🌍️ Wikipedia (FluidSynth) :
FluidSynth, connu précédemment sous le nom de Iiwusynth, est un synthétiseur virtuel temps réel qui convertit les données MIDI en un signal audio sans avoir besoin d'une carte son compatible. Il utilise la technologie des fontes sonores ("SoundFont"), c'est-à-dire des échantillons audio préchargés, en leur affectant les évènements MIDI qu'il reçoit du séquenceur.
Utilisation
FluidSynth peut agir en tant que périphérique MIDI virtuel, pouvant recevoir des données MIDI d'un programme et les transformer en audio à la volée. Il peut aussi lire directement les fichiers SMF (.mid). En sortie, les données audio peuvent être envoyées directement à un périphérique audio pour être jouées, ou sauvegardées dans un fichier (.raw, . wav). Il peut également convertir un fichier SMF en fichier audio de façon plus rapide que temps réel.
L'ensemble de ces caractéristiques permet de répondre aux besoins basiques suivants :
• Synthétiser des données MIDI vers les haut-parleurs depuis une autre application
• Synthétiser des données MIDI depuis une autre application tout en les enregistrant dans un fichier audio
• Jouer un fichier MIDI via les haut-parleurs
• Convertir un fichier MIDI vers un ficher audio.
Le projet fournit aussi une bibliothèque partagée pouvant être utilisée avec d'autres programmes. Fluidsynth est compatible avec le serveur audio jack. La taille de la banque de fontes sonores chargées est limitée par la quantité de mémoire vive disponible. Ces banques de son, au format sf2, peuvent être chargées via Qsynth, l'interface graphique libre de FluidSynth. Les deux logiciels sont disponibles dans la plupart des distributions Linux et peuvent être compilés pour Windows.
Intégration à VLC
Un module FluidSynth est intégré à VLC depuis sa version 0.9.0, permettant aux utilisateurs de ce lecteur multimédia la possibilité de lire des fichiers MIDI, une fois une bibliothèque SoundFont renseignée dans les paramètres du lecteur. Mais les utilisateurs Windows ont dû attendre la version 1.1.0 ; et même la version 1.1.6 pour les utilisateurs de Mac OS X.
La version 2.1.0 pour Windows de VLC supprime le module FluidSynth car sa dernière version utilise GLib qui est difficilement compatible avec Windows. FluidSynth reste cependant disponible pour les utilisateurs de distributions Linux.
🌍️ Wikipedia (DSSI) :
Dans le domaine de la MAO, DSSI (acronyme de Disposable Soft Synth Interface, à prononcer « dizzy ») est une interface de programmation pour le développement de plugins audio, principalement accès dans la synthèse et la disposition d'une interface utilisateur. Elle a été développée pour les besoins des applications Linux, mais conçue pour être portable.
C'est une spécification ouverte, dérivée des spécifications LADSPA afin de couvrir la synthèse d'instruments, à la manière de VSTi. Elle est constituée d'interface en langage C permettant de faire dialoguer les plugins avec leur hôte. Un plugin d'interface utilisateur est un programme indépendant, le dialogue avec le plugin de synthèse se faisant par le biais du protocole OSC.
Les spécifications LV2 ont pour vocation à regrouper et étendre LADSPA et DSSI.
🍥️ Debian:
fluidsynth
Logiciel de synthèse MIDI en temps réel
Fluidsynth est un synthétiseur MIDI en temps réel basé sur les spécifications soundfont2. Il peut être utilisé pour traiter une entrée MIDI ou des fichiers MIDI vers un périphérique audio. Les évènements MIDI sont lus à partir d'un périphérique MIDI. Le son est envoyé en temps réel au périphérique sonore de sortie.
fluidsynth-dssi
Enveloppe DSSI pour le synthétiseur SoundFont-playing de FluidSynth,
Le paquet FluidSynth-DSSI fournit FluidSynth-DSSI, une enveloppe pour le synthétiseur logiciel SoundFont-playing de FluidSynth, autorisant son fonctionnement comme greffon DSSI.
DSSI est une API pour les greffons de traitement audio, particulièrement utile pour les greffons de synthèse logicielle avec interface graphique.